Are you over 50 and experiencing foot pain that’s getting worse each day? You’re not alone; older adults suffer from chronic foot pain, and it often worsens with age.
Your feet have carried you through life, but aging brings unique challenges. From plantar fasciitis to arthritis, seniors face common foot problems that can limit mobility and reduce quality of life.
The good news? Most foot problems can be prevented or effectively treated with the right knowledge and care. Understanding why your feet age differently and knowing the warning signs can help you stay active and pain-free.
Keep reading to learn about the most common senior foot issues, why they happen, and simple solutions to keep you moving comfortably through your golden years.
Why Are Seniors More Prone to Foot Troubles?
1. Natural Structural Changes in Feet-Aging causes feet to widen, arches to flatten, and protective fat padding to decrease. These changes reduce shock absorption, making feet vulnerable to pain.
2. Weakened Muscles and Stiff Joints- Muscle mass declines, and joints stiffen with age. This combination reduces flexibility and strength, making the feet less functional and more prone to injury.
3. Skin Changes and Reduced Healing- Aging skin becomes thinner, drier, and less elastic. Natural oils decrease, causing cracking. Healing also takes longer in older adults.
4. Decreased Blood Circulation- Blood flow to the feet naturally decreases with age. Poor circulation slows healing, reduces oxygen delivery, and increases the risk of infection in foot tissues.
5. Higher Risk of Chronic Health Conditions- Seniors develop diabetes, arthritis, and circulation problems more often. These conditions cause nerve damage, reduce blood flow, and increase the risk of foot complications.
22 Most Frequent Foot Issues in Older Adults
Older adults face a wide range of foot problems that can affect mobility and quality of life. Here are the most common conditions seniors experience, along with simple solutions to manage each issue.
1. Plantar Fasciitis
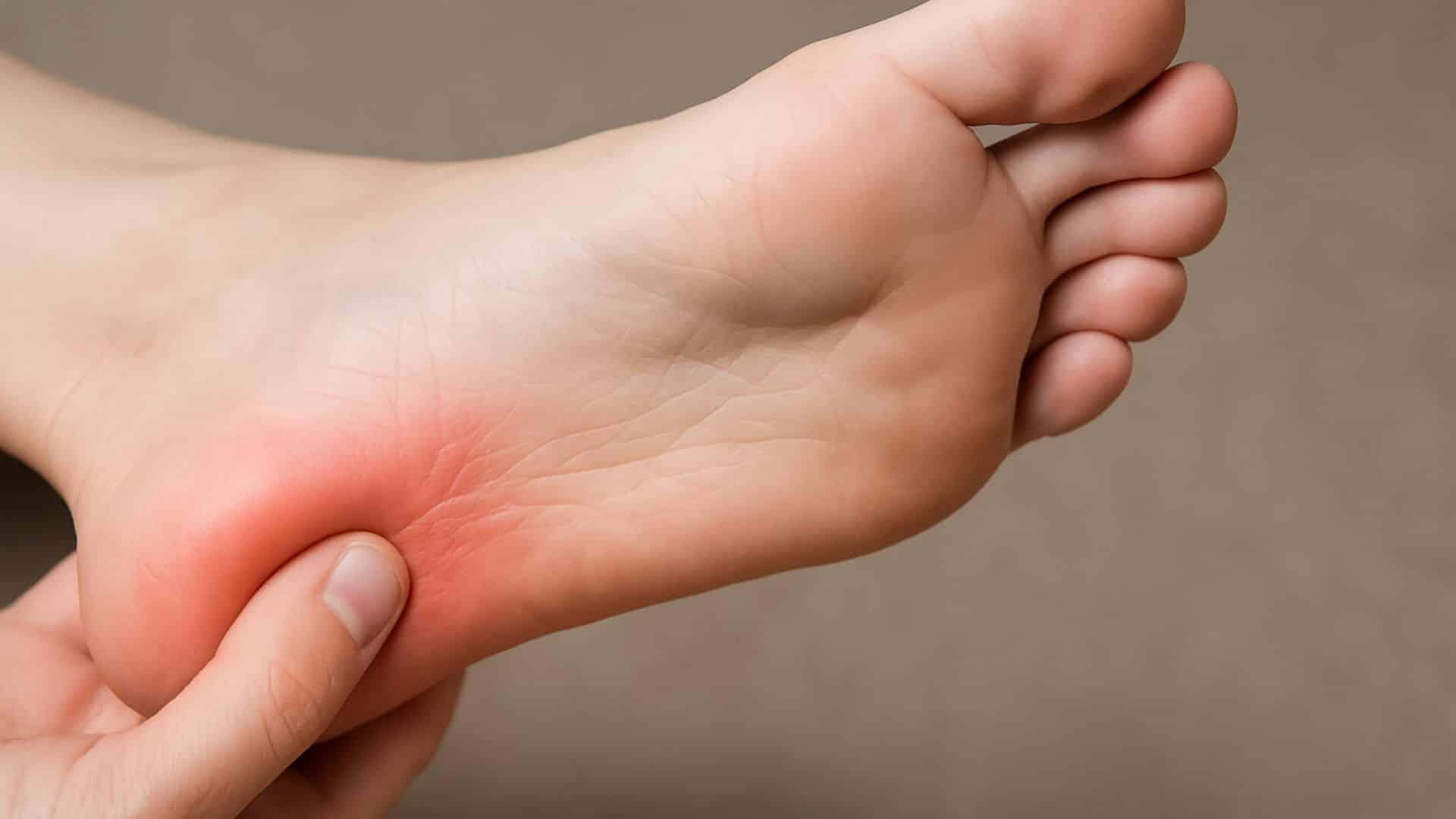
This condition causes sharp heel pain when the tissue connecting your heel to your toes becomes inflamed. Pain is often worse in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting. It especially affects adults over 50.
The pain typically occurs because the plantar fascia tissue tightens as you sleep overnight. Walking after rest stretches this tissue suddenly, causing sharp stabbing sensations.
Quick Fix: Wear supportive shoes with Good Arch Support and Cushioning.
2. Arthritis (osteoarthritis)
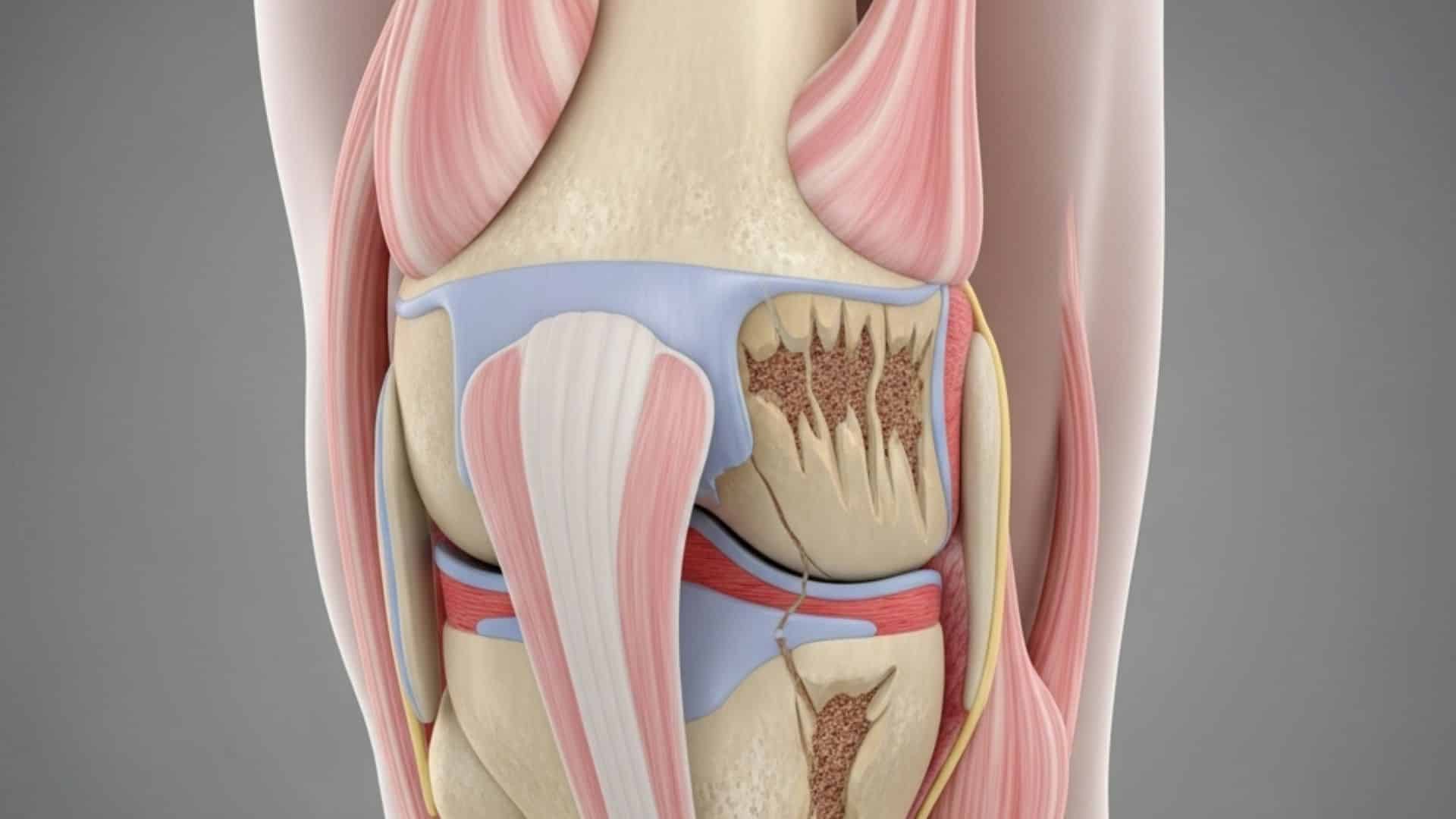
Joint pain and stiffness develop when protective cartilage wears down over time. About 17% of adults over 50 experience foot arthritis. Symptoms include reduced flexibility, swelling, and grinding sensations in joints.
Weather changes can make arthritis pain worse, and morning stiffness is common. The condition often affects multiple joints in the foot simultaneously.
Quick Fix: Take Anti-Inflammatory Medications and Avoid High-Impact Activities.
3. Bunions
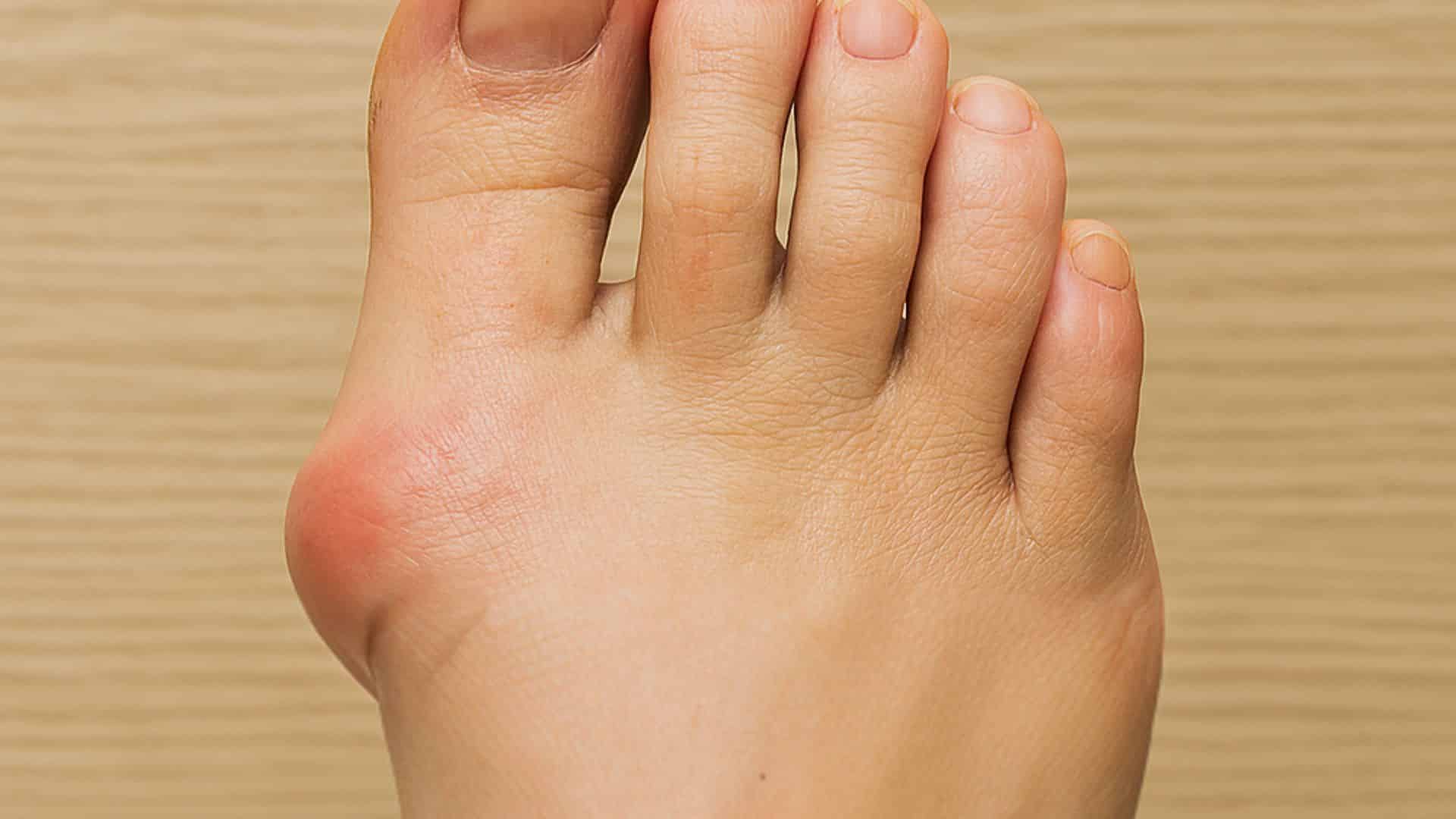
Painful bony bumps form when the big toe leans toward other toes. They appear more often in women and can run in families. The condition causes crowding of other toes and difficulty wearing shoes.
Bunions develop slowly over the years and can become red, swollen, and tender. Wearing high heels or narrow shoes can speed up their formation.
Quick Fix: Wear Flat Shoes with Plenty of Toe Space.
4. Hammertoe
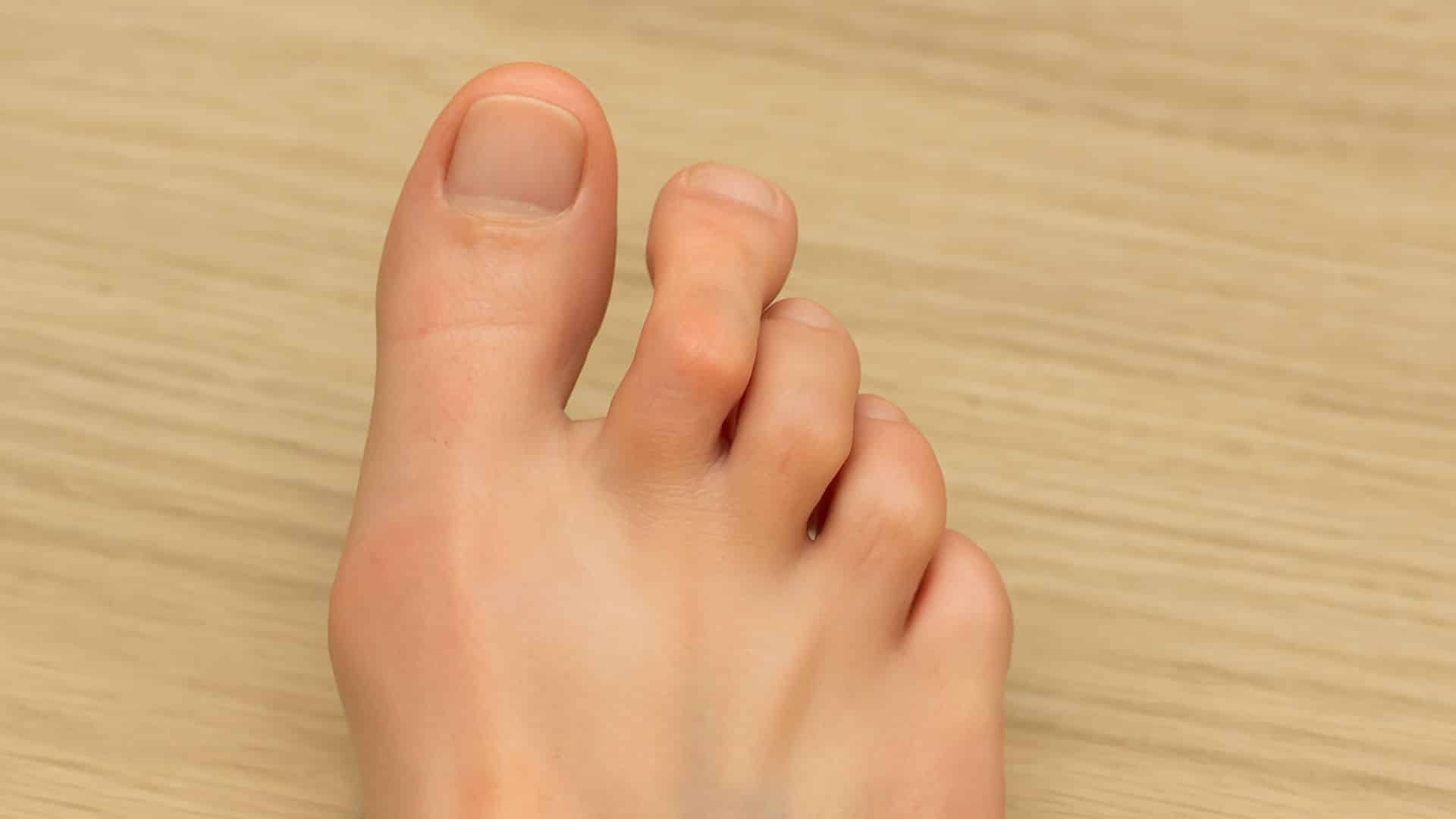
The middle joint of your toe bends abnormally, usually affecting the second toe. This creates a hammer-like appearance and often develops alongside bunions. Corns and calluses commonly form from shoe rubbing.
The bent-toe position makes it difficult to find comfortable shoes. Left untreated, the joint can become rigid and require surgery.
Quick Fix: Avoid tight, Narrow Shoes and High Heels.
5. Claw Toe
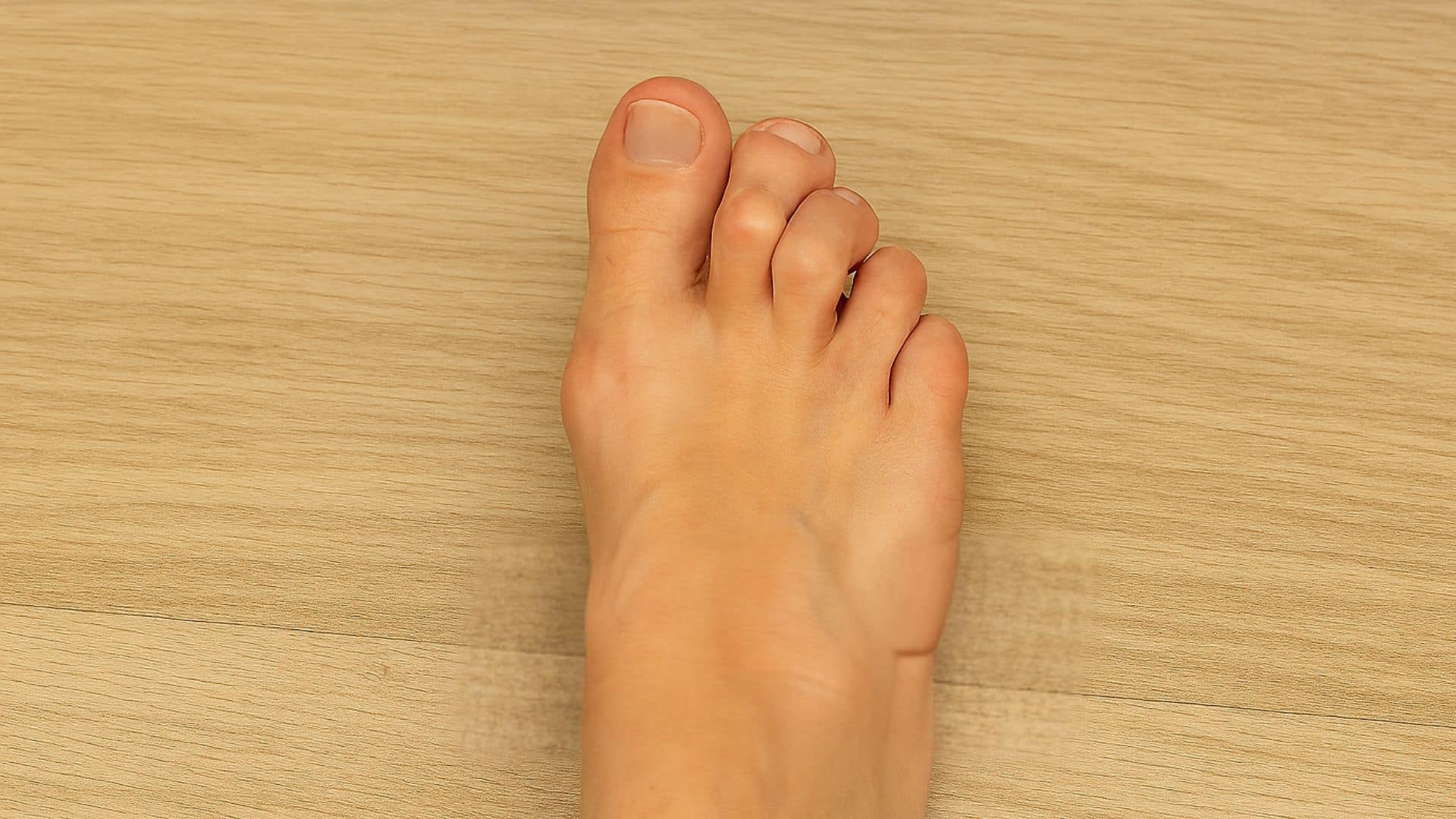
Multiple toes bend into a claw-like position, with joints pointing up and down. This condition often affects four smaller toes simultaneously and makes walking difficult. It can result from muscle imbalances.
Claw toes create pressure points that lead to painful corns on top of the toes. The condition makes it hard to wear normal shoes comfortably.
Quick Fix: Do Toe Stretches and Strengthening Exercises Daily.
6. Corns and Calluses
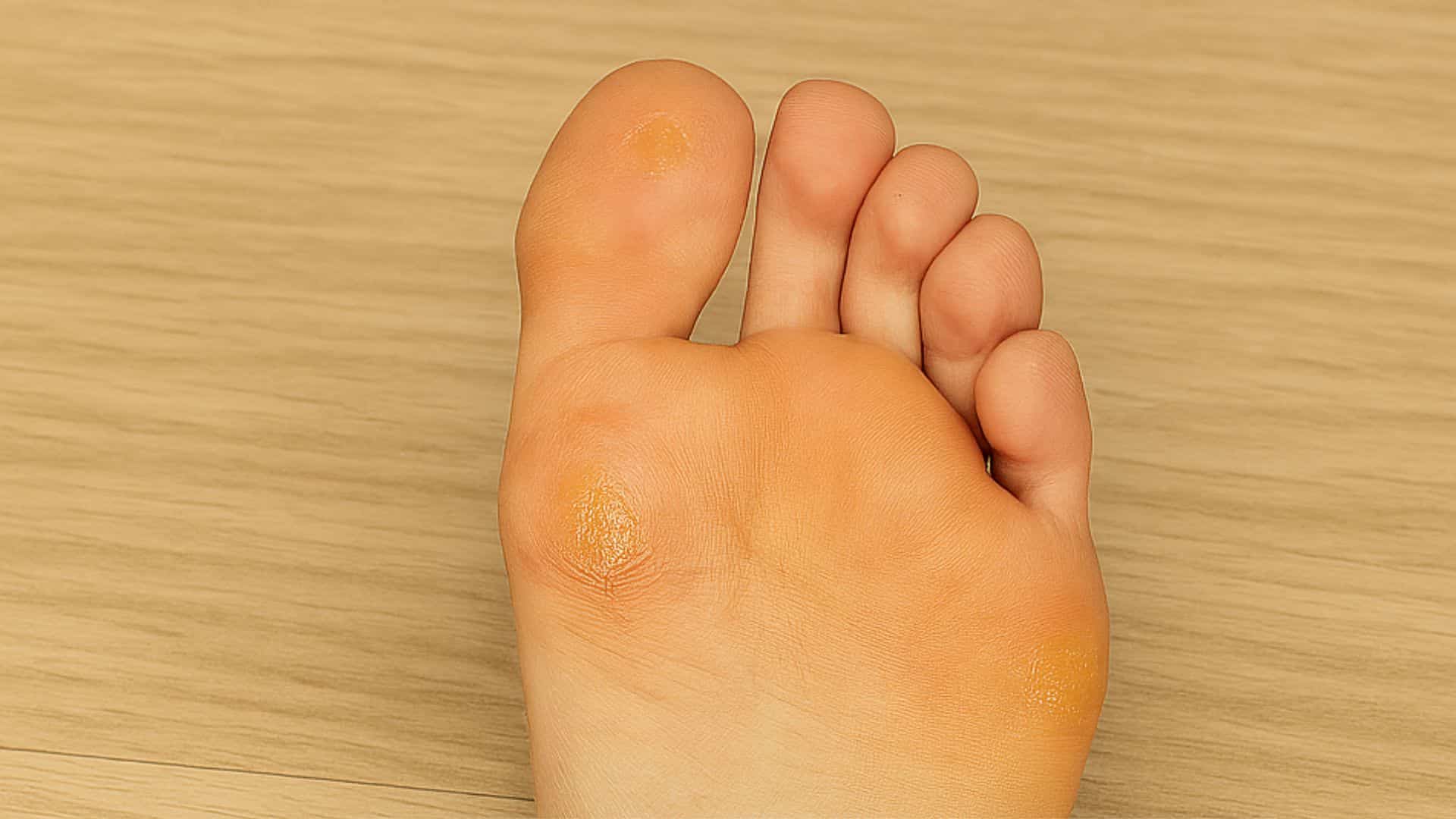
Thickened skin patches develop from repeated friction and pressure. Corns are smaller with hard centers, while calluses are larger and usually painless. Both conditions worsen with improper footwear.
Corns often form on the toes tops and sides, while calluses appear on weight-bearing areas. Both can become painful if they grow too thick.
Quick Fix: Soak feet in Warm Water and Gently Remove Dead Skin with A Pumice Stone.
7. Heel Pain (Fat Pad Atrophy)
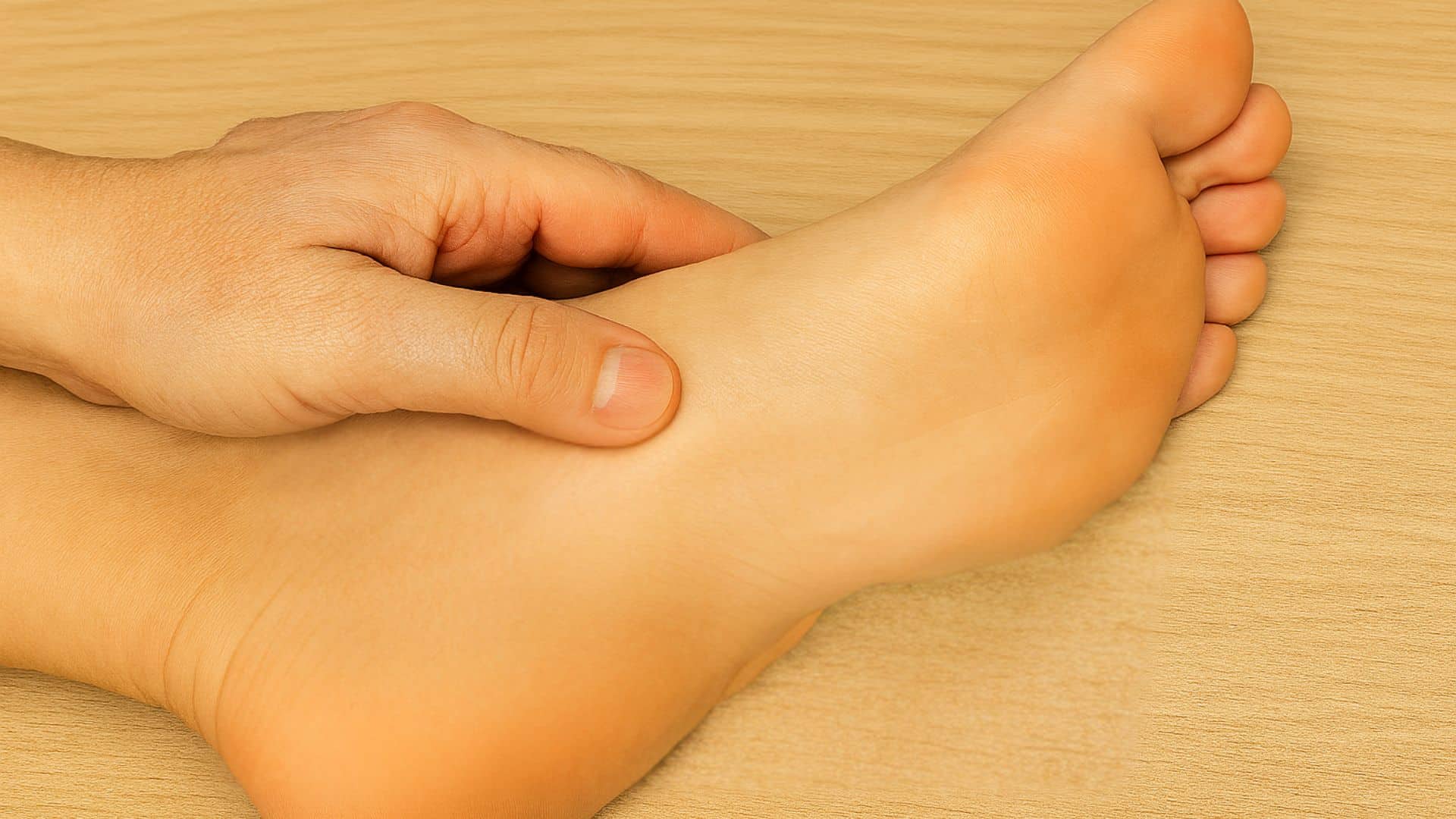
The protective fat cushioning in your heel thins out, causing bruise-like pain. About 30% of Americans over 60 develop this condition. It feels like walking on bones without cushioning.
The pain is usually worse on hard surfaces and improves with rest. Morning steps can be particularly painful until the foot warms up.
Quick Fix: Use Heel Cups and Cushioned Shoe Inserts for Support.
8. Fungal Infections
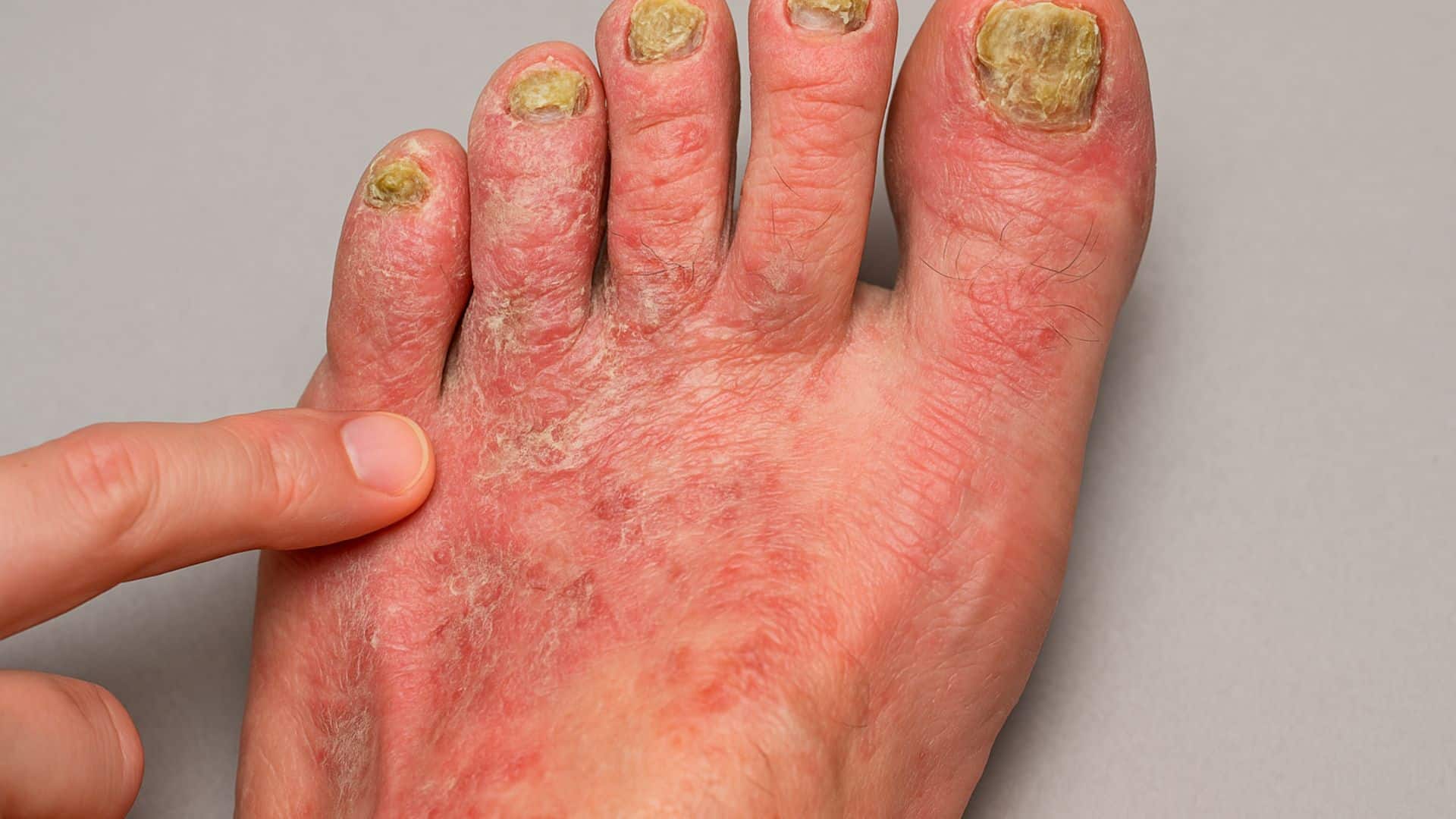
Athlete’s foot and toenail fungus thrive in warm, moist environments. About 50% of adults over 60 contract fungal infections. Symptoms include itching, burning, peeling skin, and thick, discolored nails.
Fungal infections spread easily in public areas like pools and locker rooms. They can take weeks or months to clear completely with treatment.
Quick Fix: Keep Feet Clean and Dry, Use Antifungal Powder.
9. Gout
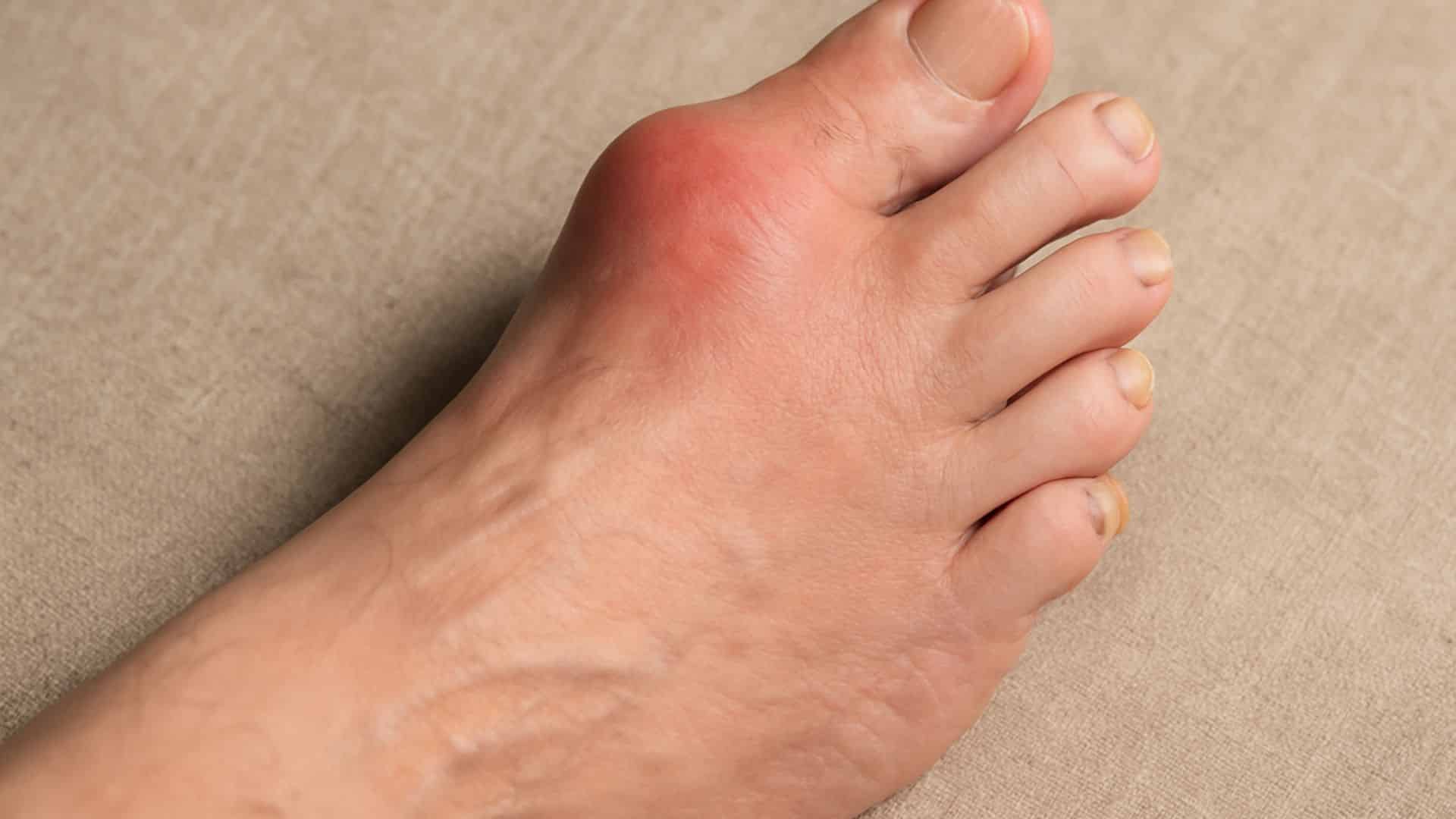
Uric acid crystals form in joints, causing intense pain and swelling, often in the big toe. This painful arthritis affects nearly 4% of US adults and is more common in men over 40.
Gout attacks can last for days and make walking extremely difficult. The affected joint becomes red, hot, and swollen during flare-ups.
Quick Fix: Limit Alcohol, Red Meat, and Shellfish Consumption.
10. Diabetic Foot Complications
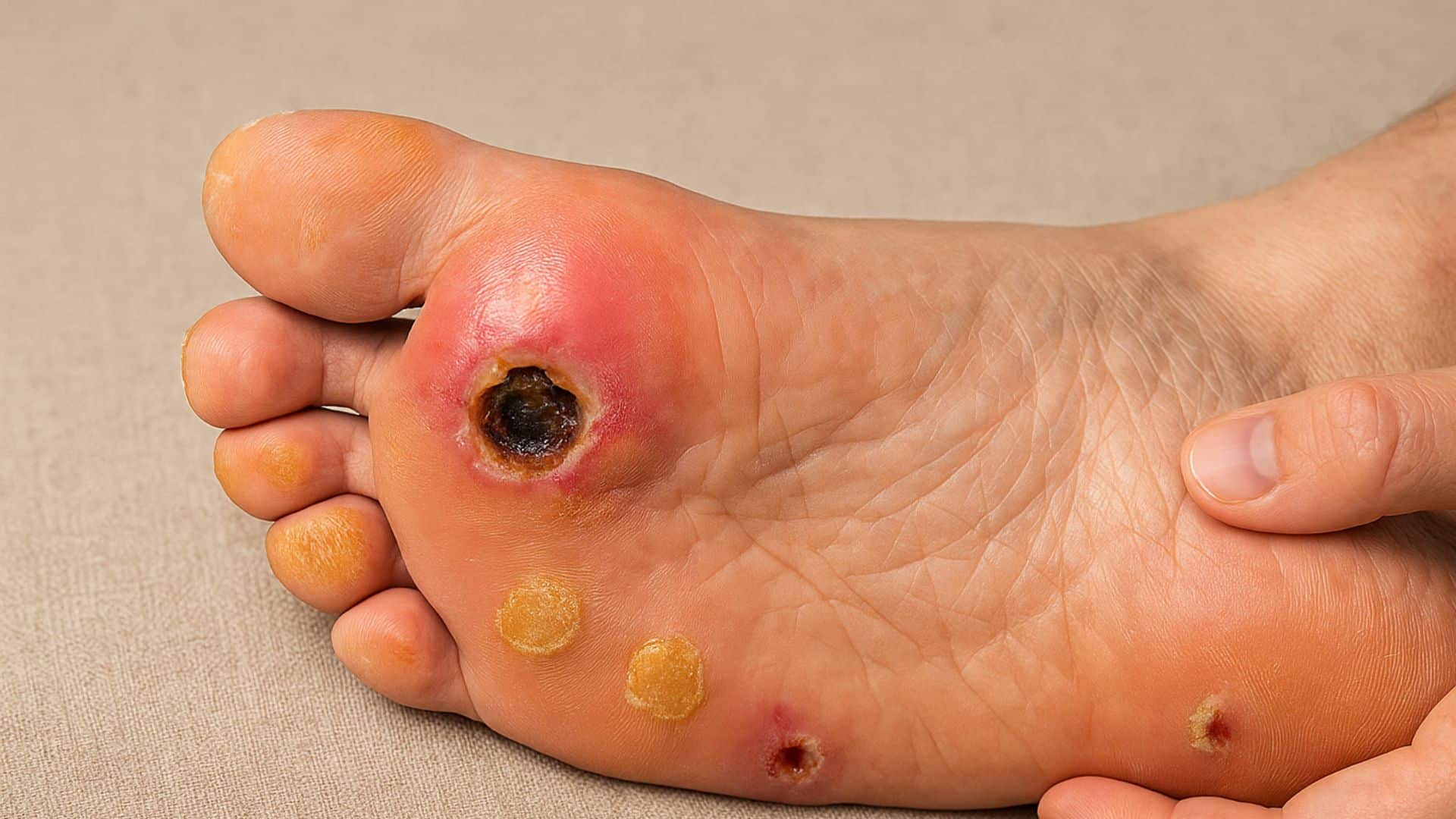
Diabetes damages nerves and reduces blood flow, leading to numbness and slower healing. Complications include neuropathy, poor circulation, and foot shape changes. Infections can become serious quickly.
People with diabetes may not feel cuts or sores, allowing infections to develop unnoticed. Regular foot checks are essential for early problem detection.
Quick Fix: Check Feet Daily for Cuts, Sores, or Changes.
11. Flat Feet (fallen Arches)
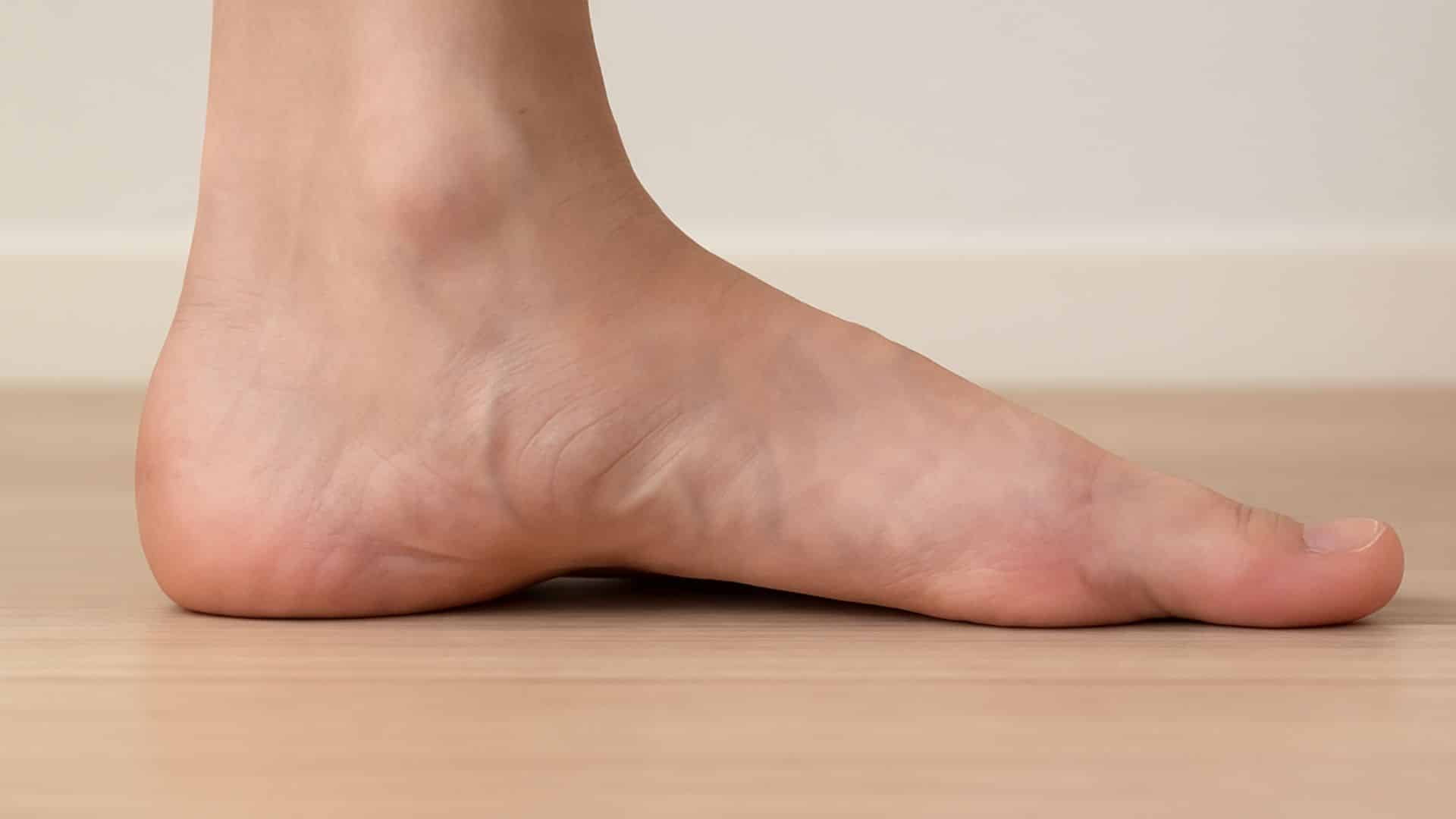
Foot arches flatten or collapse, affecting 30% of the population. The posterior tibial tendon weakens over time, causing pain and visible foot shape changes. This condition is most common in women over 40.
Flat feet can cause pain in the arch, heel, or ankle areas. The condition may worsen over time without proper support.
Quick Fix: Wear shoes with Proper Arch Support and Orthotics.
12. Ingrown Toenails
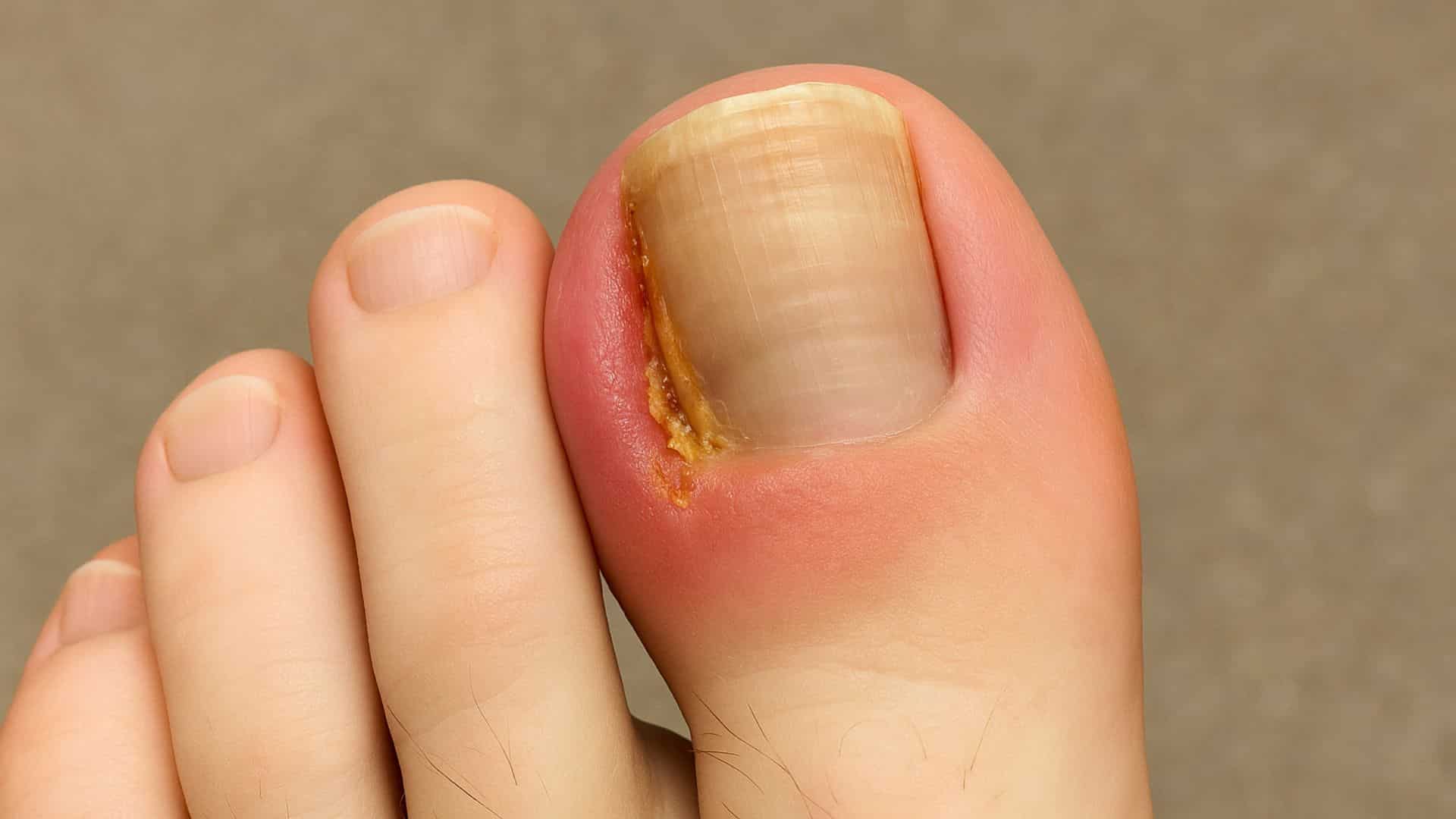
Nail edges grow into the surrounding skin, causing pain, swelling, and possible infection. This problem is more common in older adults and can be worsened by tight shoes or improper nail trimming.
The big toe is most commonly affected, and infections can develop quickly. Proper nail care prevents most ingrown toenail problems.
Quick Fix: Cut toenails Straight Across and Avoid Tight Shoes.
13. Achilles Tendonitis
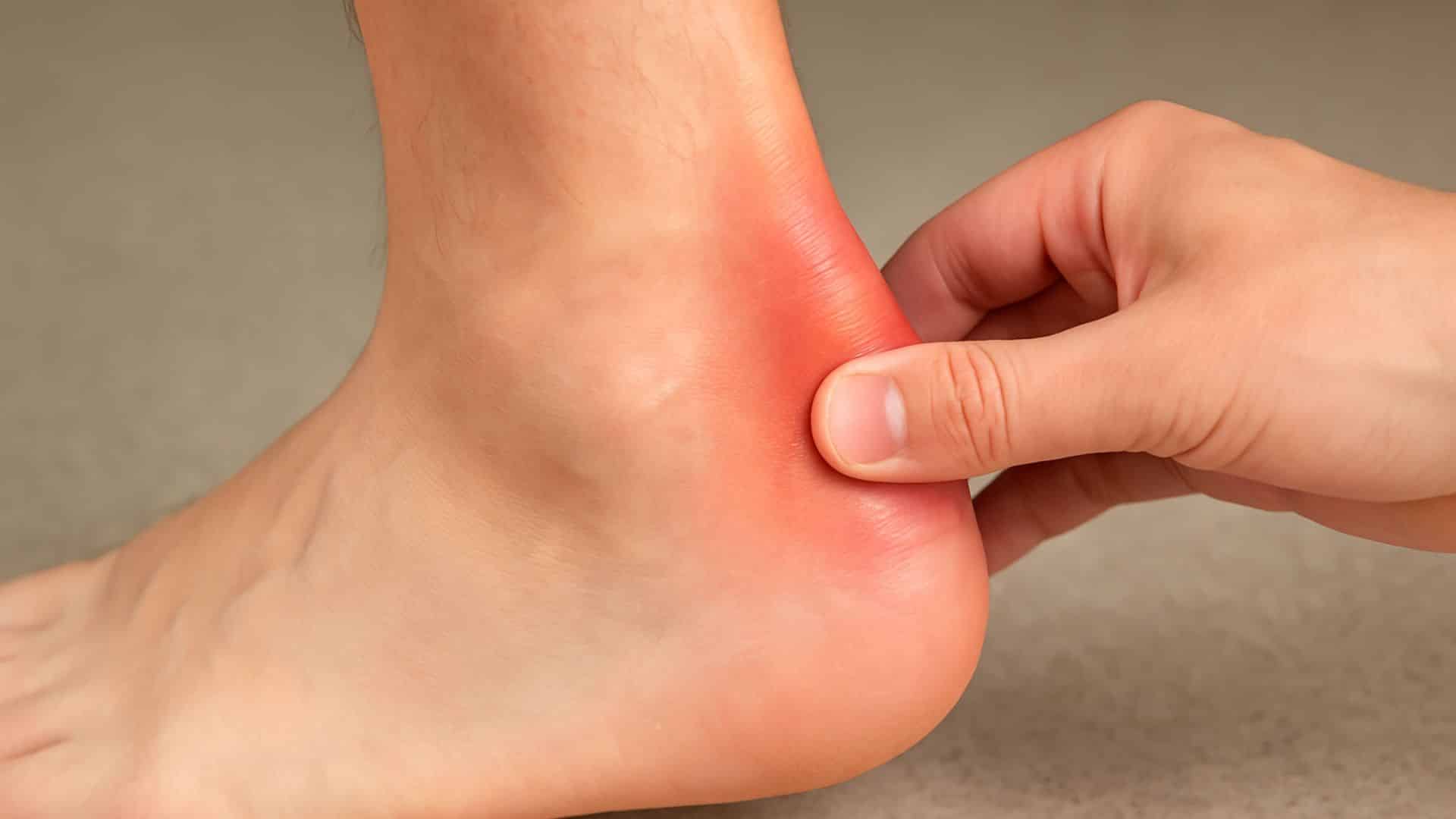
The tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone becomes inflamed. Age weakens this tendon, making it more susceptible to injury. Pain occurs in the heel or the back of the ankle.
Morning stiffness is common, and pain may worsen with activity. The condition can become chronic if not treated properly.
Quick Fix: Rest the Affected Foot and Apply Ice to Reduce Swelling.
14. Morton’s Neuroma
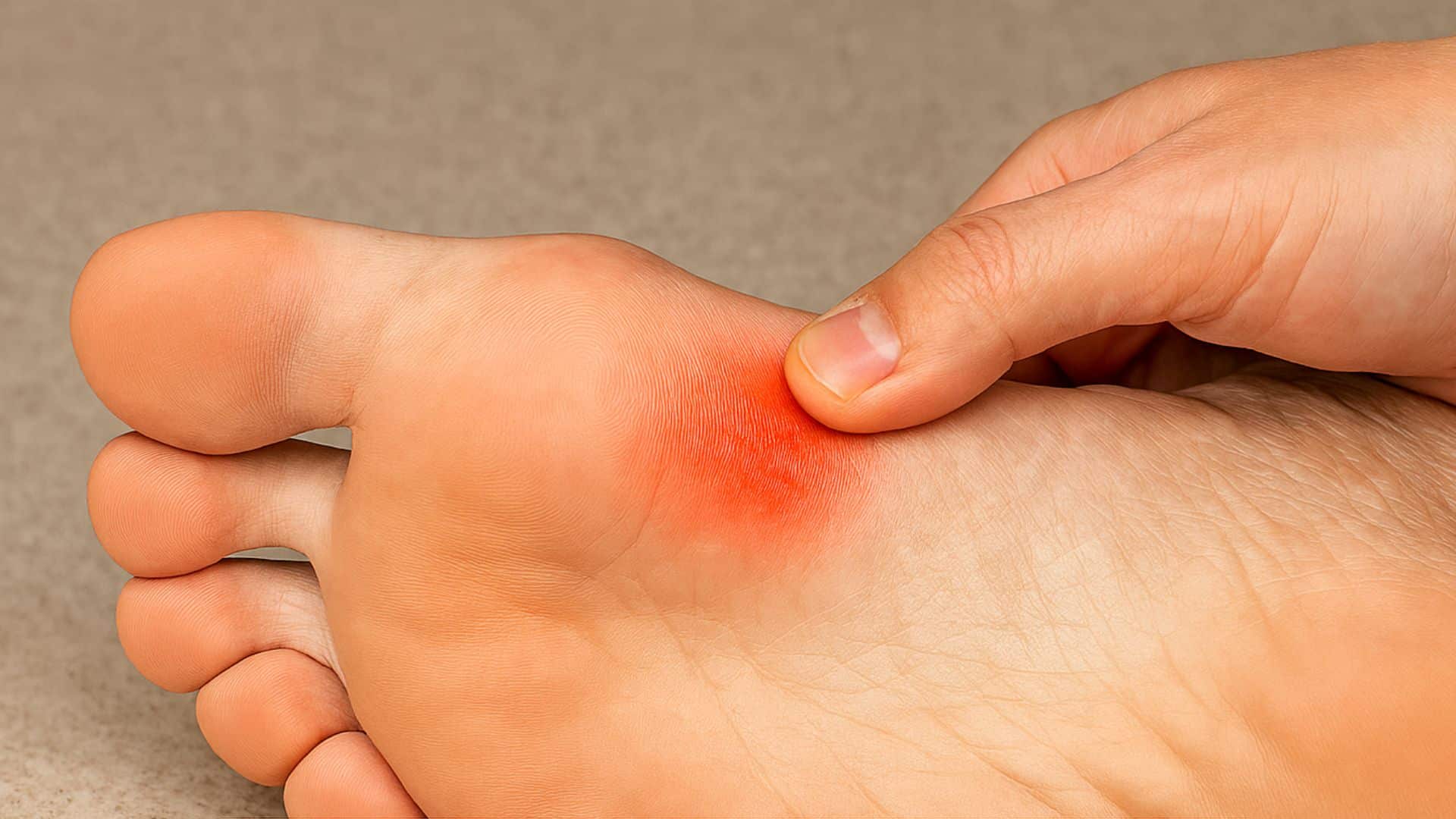
The tissue around the foot nerves thickens, causing sharp burning pain between the toes. About 30-33% of people experience this condition. It often feels like standing on a pebble in your shoe.
The pain typically occurs between the third and fourth toes. Removing shoes and rubbing the area may provide temporary relief.
Quick Fix: Wear shoes with Wide Toe Boxes and Avoid High Heels.
15. Stress Fractures
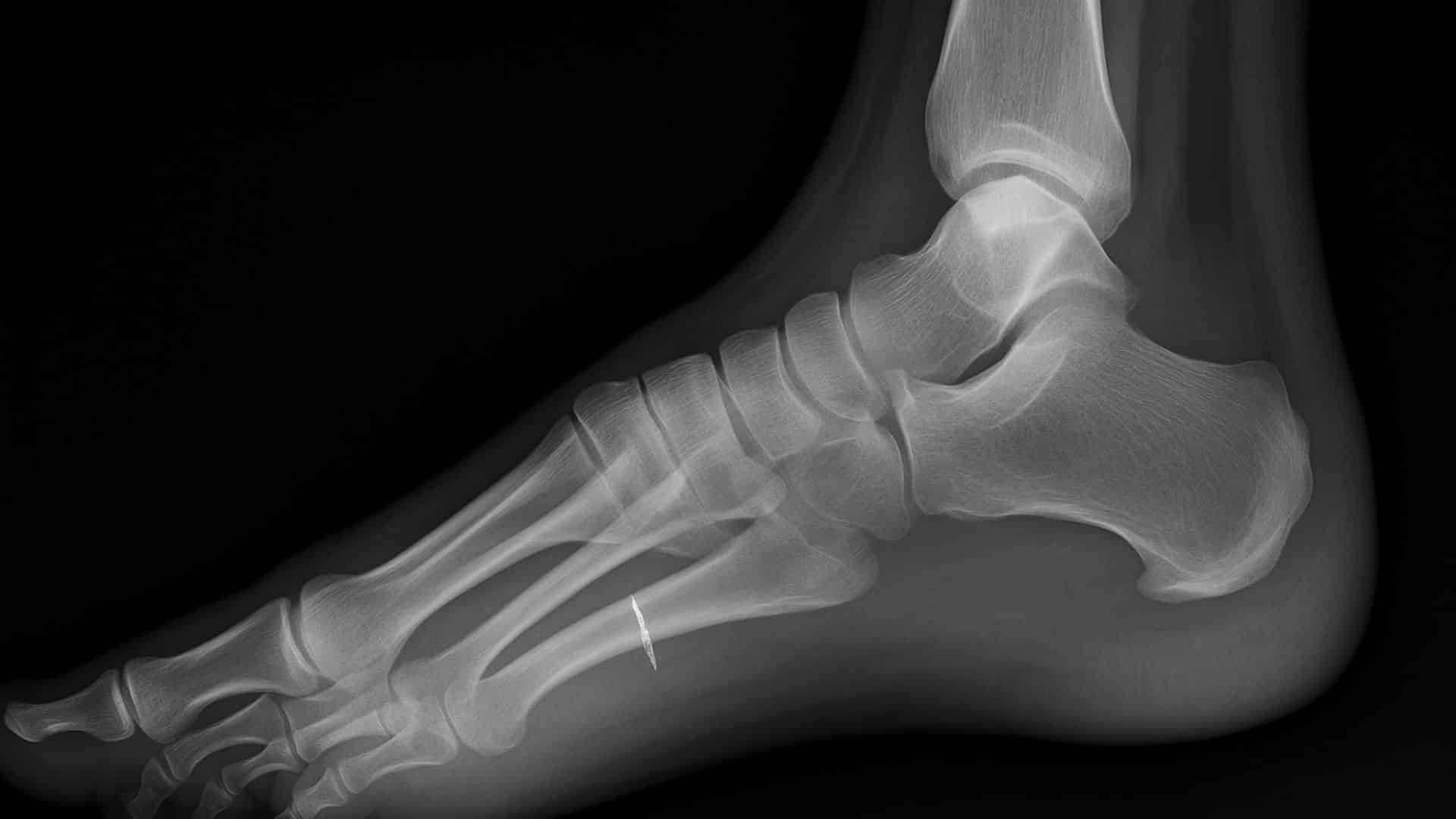
Tiny cracks develop in foot bones from repetitive force or overuse. These are common in weight-bearing bones and are more likely in older adults with weakened bones or vitamin D deficiency.
Pain from stress fractures starts gradually and worsens with activity. The second and third toe bones are most commonly affected.
Quick Fix: Rest from Weight-Bearing Activities and Wear Protective Boots.
16. Ankle Sprains
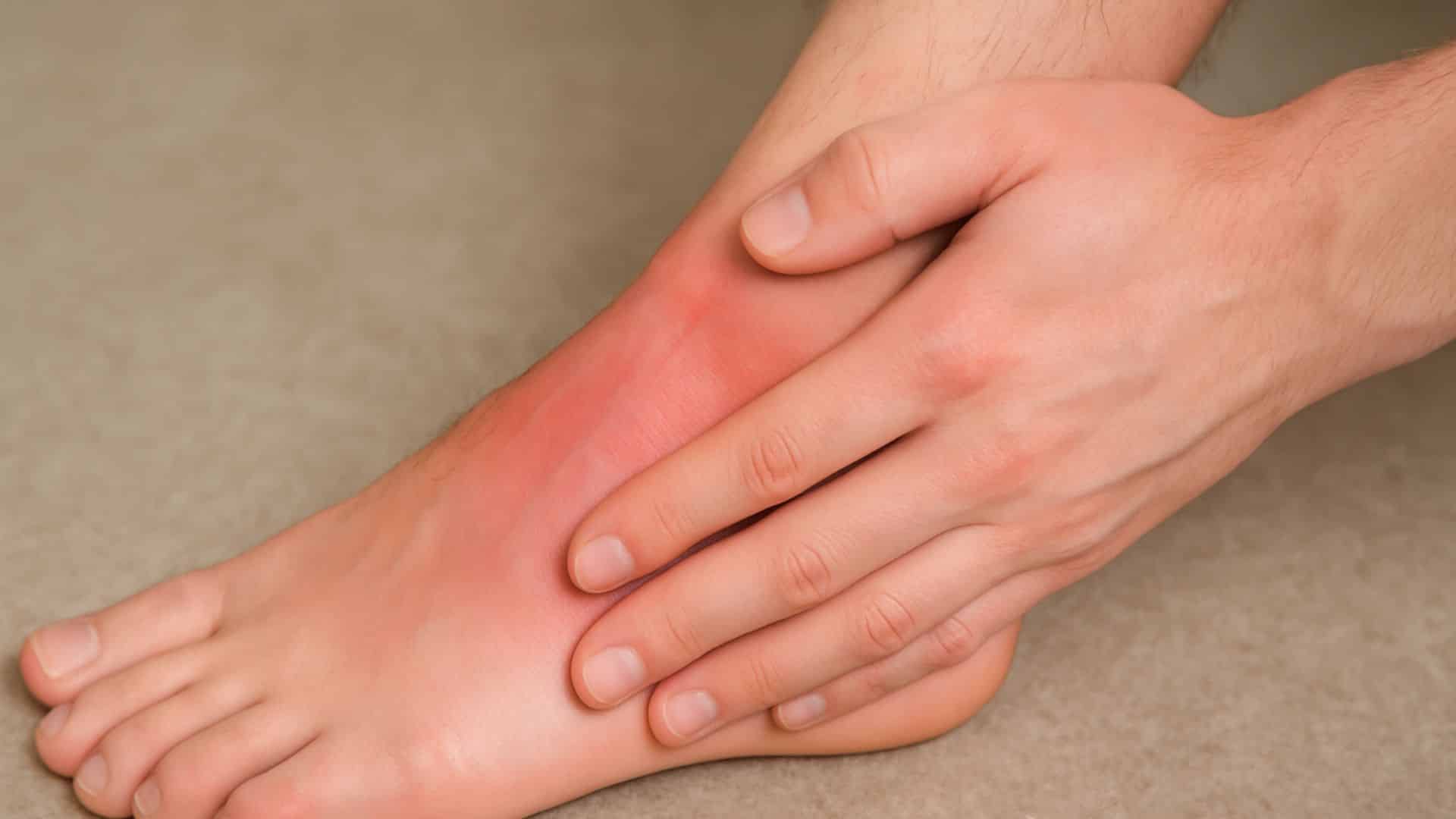
Ligaments stretch or tear when the ankle twists awkwardly. About 80% of people experience ankle sprains during their lifetime. Risk increases with age due to balance issues and weakened muscles.
Most sprains affect the outside of the ankle when the foot rolls inward. Proper healing prevents future instability and repeat injuries.
Quick Fix: Rest, Ice, Compress, and Heighten the Injured Ankle.
17. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
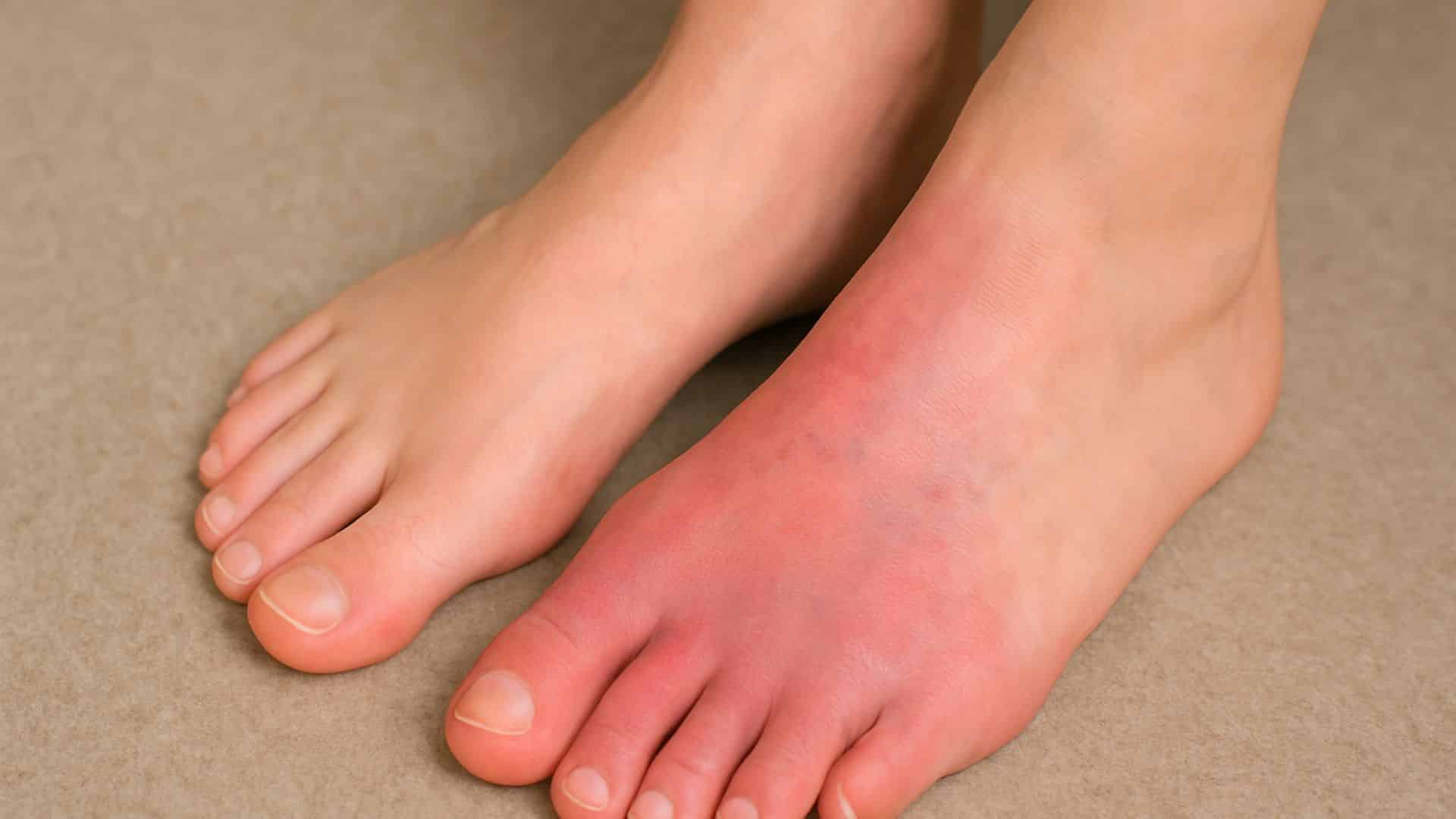
Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the feet and legs. This affects 5-10% of older adults and can cause burning pain, especially at night. Poor circulation slows healing and increases infection risk.
Symptoms include leg cramping during walking that improves with rest. The condition requires medical management to prevent serious complications.
Quick Fix: Engage in Regular Exercise and Avoid Smoking.
18. Edema (swelling)
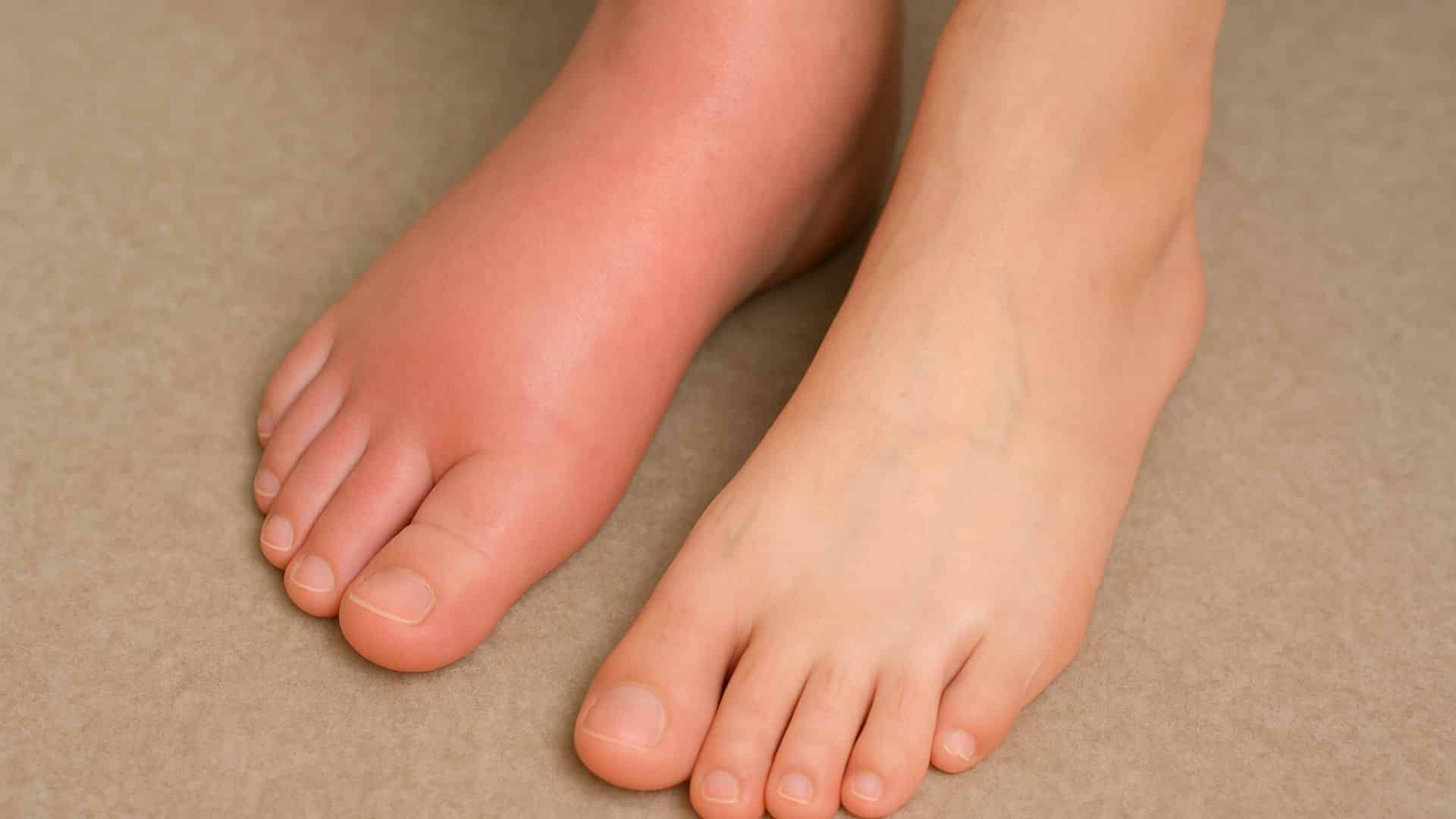

Fluid buildup causes ankle, foot, or leg swelling. Most older adults experience edema from various causes, including prolonged sitting, high sodium intake, or medical conditions.
Swelling is often worse at the end of the day and may improve overnight. Heart, kidney, or liver problems can cause persistent swelling.
Quick Fix: Climb legs when sitting and Reduce Salt Intake.
19. Bursitis
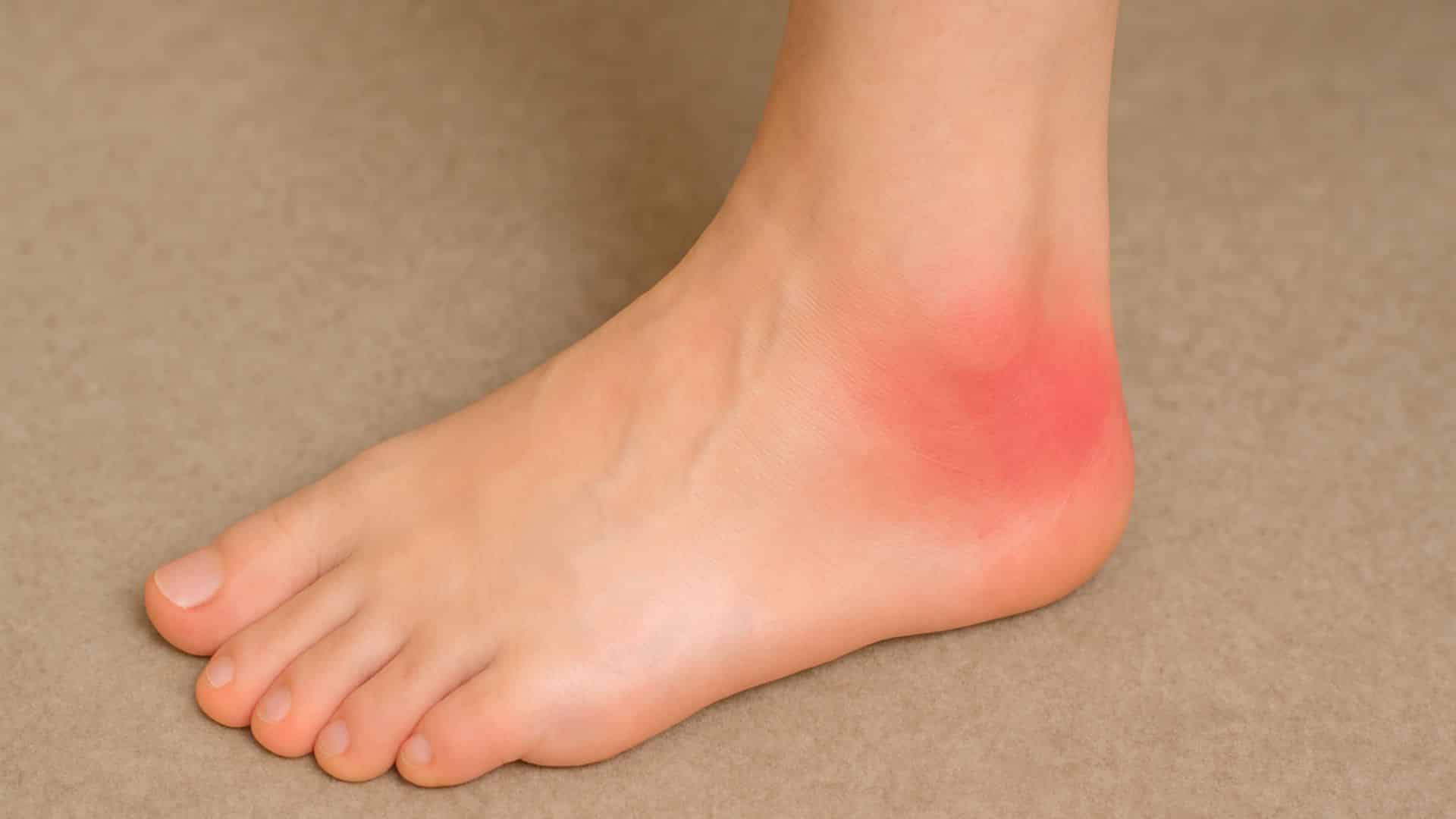
Small fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints become inflamed. This condition commonly affects the heel area in older adults and causes intense pain that worsens with movement or pressure.
The pain is often described as aching or burning and may be worse at night. Repetitive activities can trigger bursitis flare-ups.
Quick Fix: Apply ice and Avoid Activities that stress the Affected Joint.
20. Bone Spurs
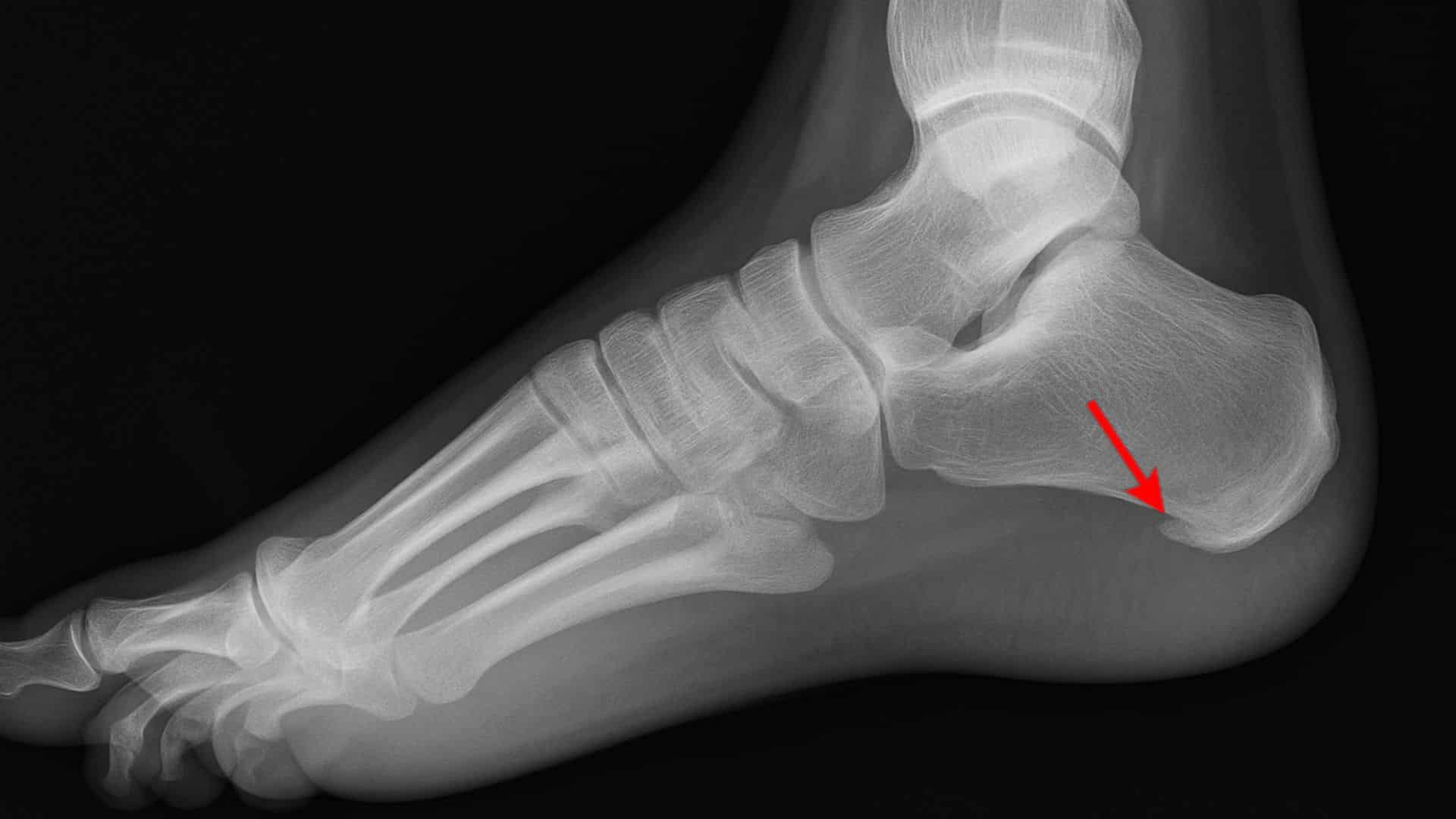
Bony projections form along bone edges, often due to arthritis. Nearly 60-80% of people over 50 develop bone spurs. They cause sharp, stabbing foot pain and difficulty walking.
Bone spurs can form anywhere in the foot but commonly affect the heel and toe joints. They may not cause pain until they rub against other bones or soft tissues.
Quick Fix: Wear shoes with Good Arch Support and maintain a Healthy Weight.
21. Cracked Heels
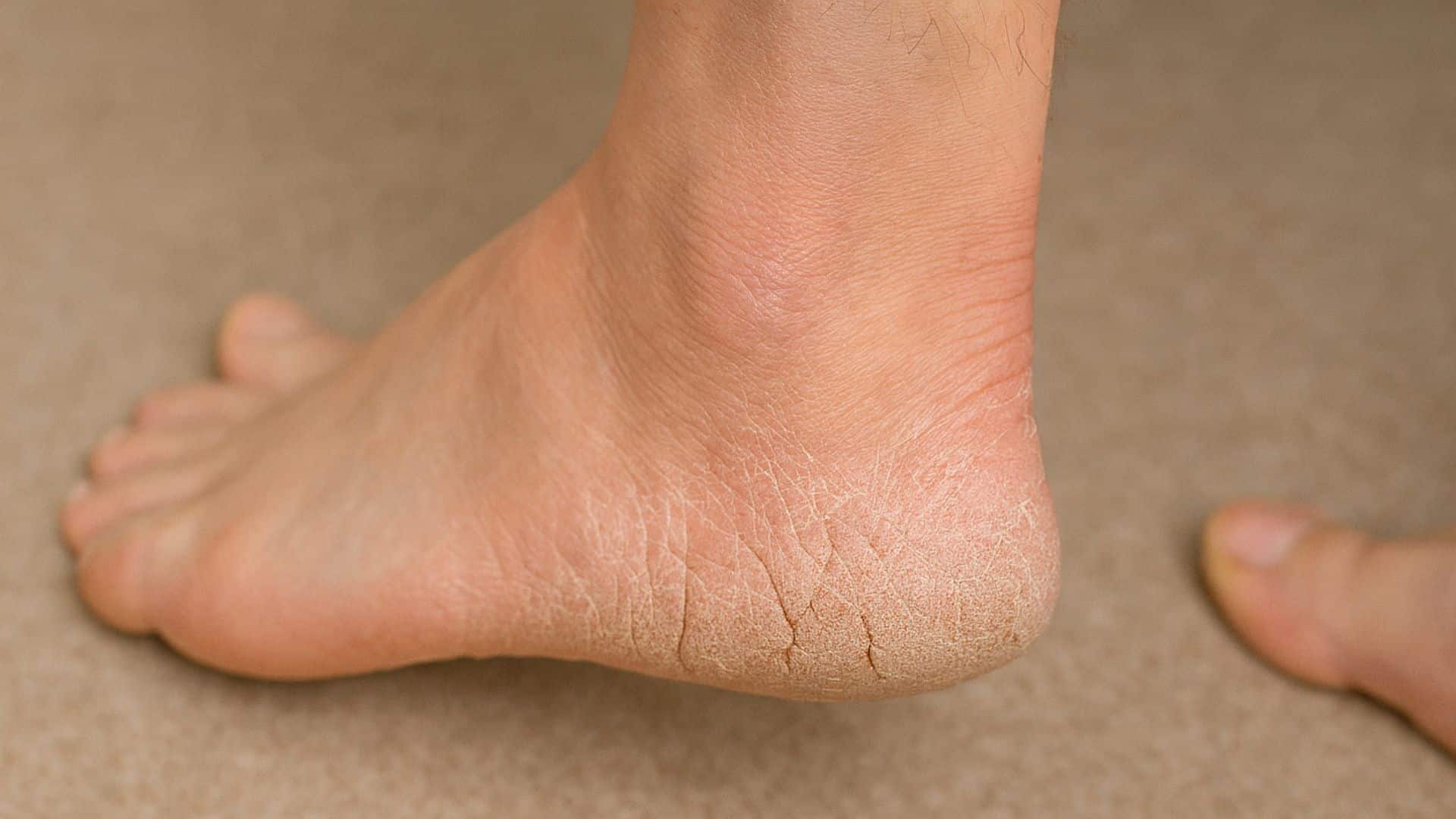
Dry, hard skin around the heels develops visible cracks. This affects adults over 21, particularly women. Aging naturally decreases skin moisture, making older adults more susceptible.
Deep cracks can bleed and become infected if not treated. The condition is often worse in winter when
humidity is low.
Quick Fix: Apply Thick Moisturizer Daily and Use Pumice Stone Gently.
22. Skin Cancer
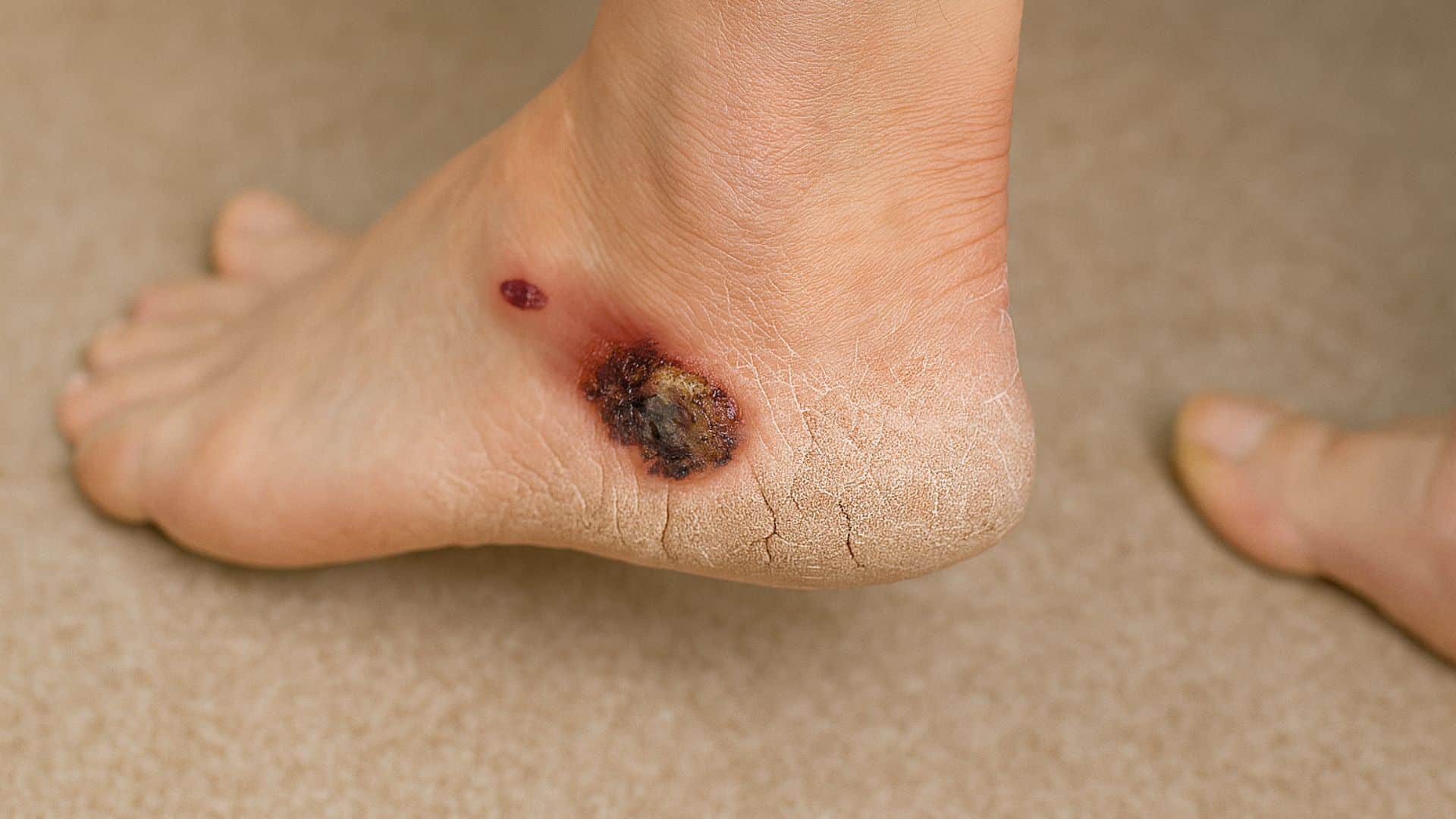
Abnormal skin cell growth can occur on the feet, often going unnoticed. Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer daily. Foot skin cancer is concerning because it’s frequently overlooked.
Melanoma on the feet is particularly dangerous because it’s often found late. Check between toes and on the soles regularly for changes.
Quick Fix: Check Feet Regularly for Changes in Moles or Skin Spots.
Why Do Feet Age Differently Than the Rest of the Body?

Your feet go through unique changes as you age that set them apart from other body parts. The aging process affects your feet in specific ways that make them more vulnerable to problems.
Physical Changes That Make Feet Age Faster
The foot structure undergoes several distinct changes over time. Your feet may widen and lose their natural arch support.
The protective fat padding in your soles decreases, leaving less cushioning for daily impact. Joint stiffness develops, reducing flexibility and the ability to absorb shock.
Muscle mass and strength decline in your feet, making them weaker. The skin becomes thinner, drier, and less elastic. These changes happen because your feet bear your full body weight every day and take thousands of steps.
Why Are Feet More Vulnerable?
Your feet experience constant wear and tear from walking, standing, and supporting your body weight. Blood circulation to your feet can decrease with age, slowing healing and making infections more likely.
The combination of reduced fat padding, weaker muscles, and daily stress makes feet age differently than other body parts that don’t face the same constant pressure and use.
Conclusion
Foot problems affect millions of seniors, but most conditions are manageable with proper care. The 25 issues we covered show how aging changes your feet in specific ways that require attention.
Prevention works better than treatment. Daily foot inspections help catch problems early when they’re easier to fix. Proper footwear makes the biggest difference – shoes with good support, cushioning, and room for your toes prevent many complications.
Don’t ignore pain or changes in your feet. What starts as minor discomfort can become serious mobility issues. See a doctor for persistent problems, especially if you have diabetes or circulation issues.
Follow simple daily habits keep your feet healthy. Your feet have supported you for decades – now it’s time to support them back.
What foot concern troubles you most? Take action today for healthier, more comfortable feet tomorrow.








